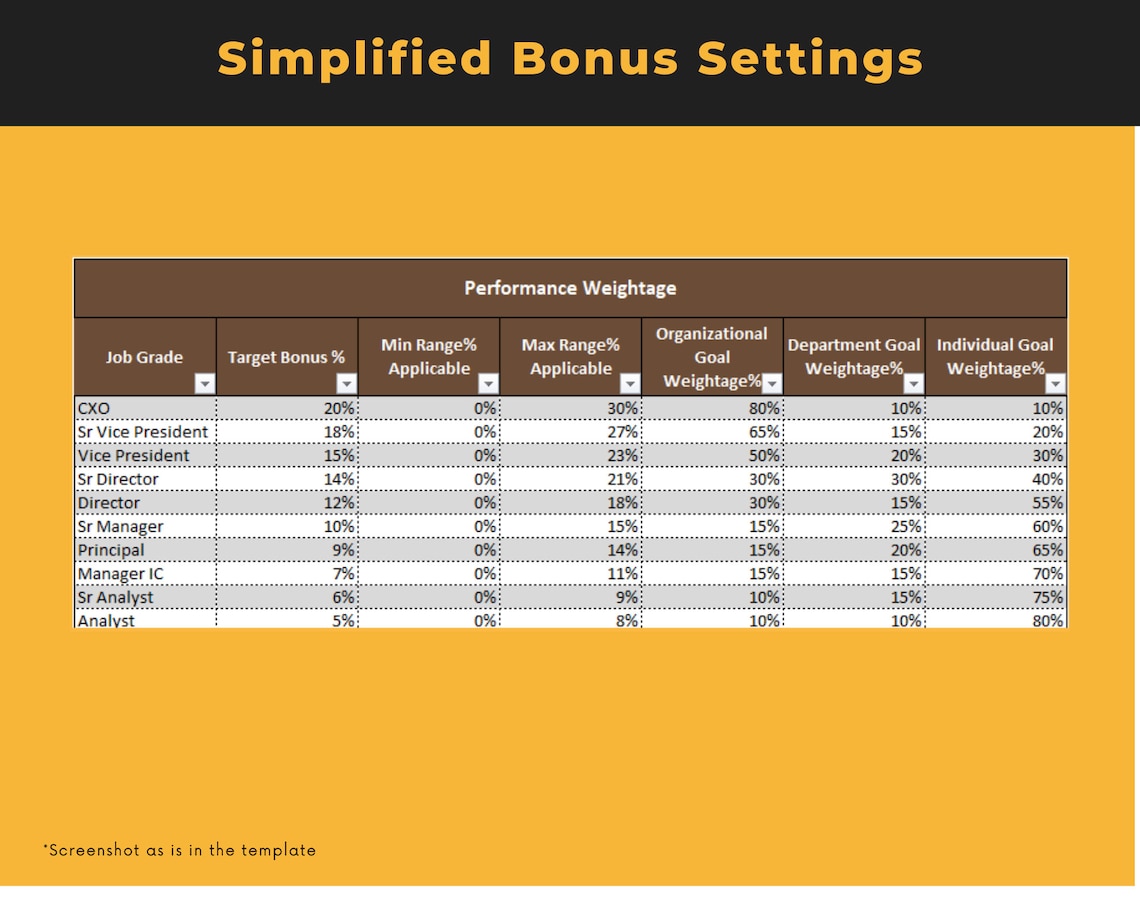
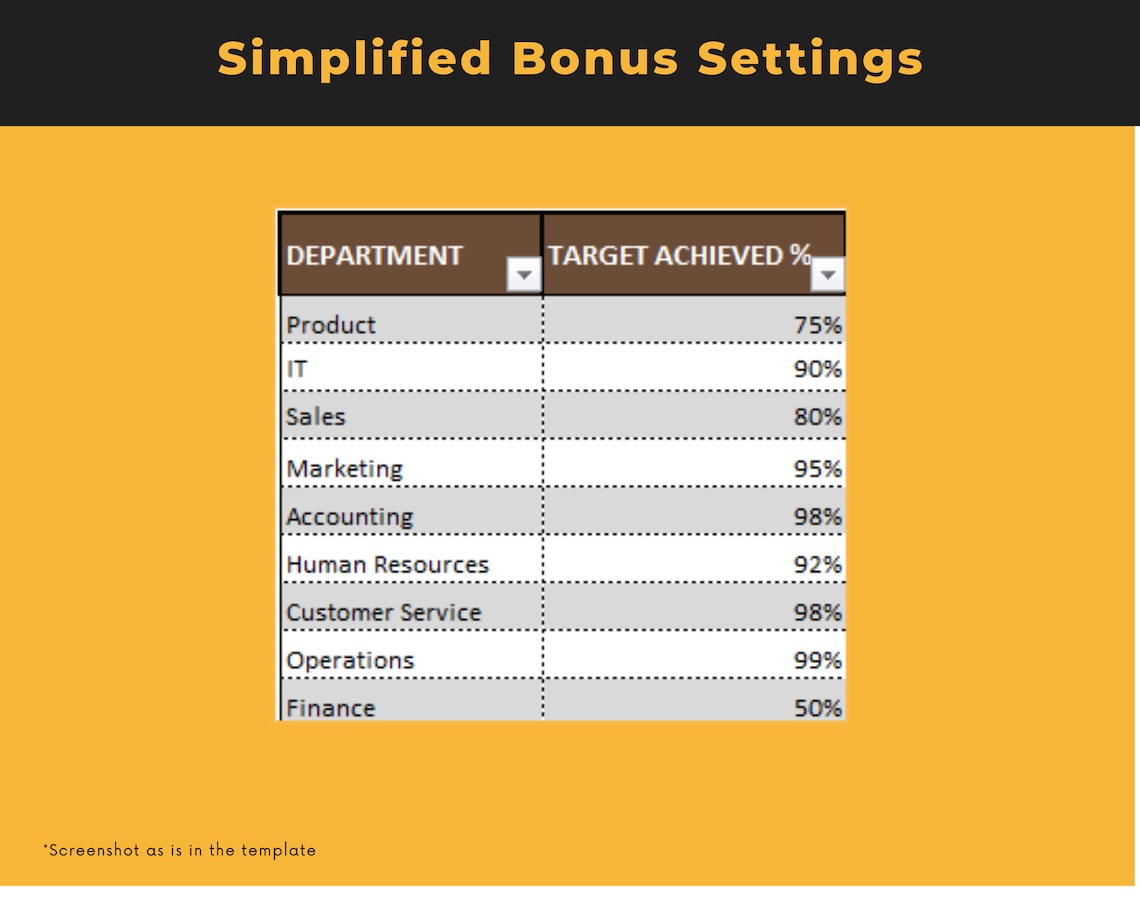
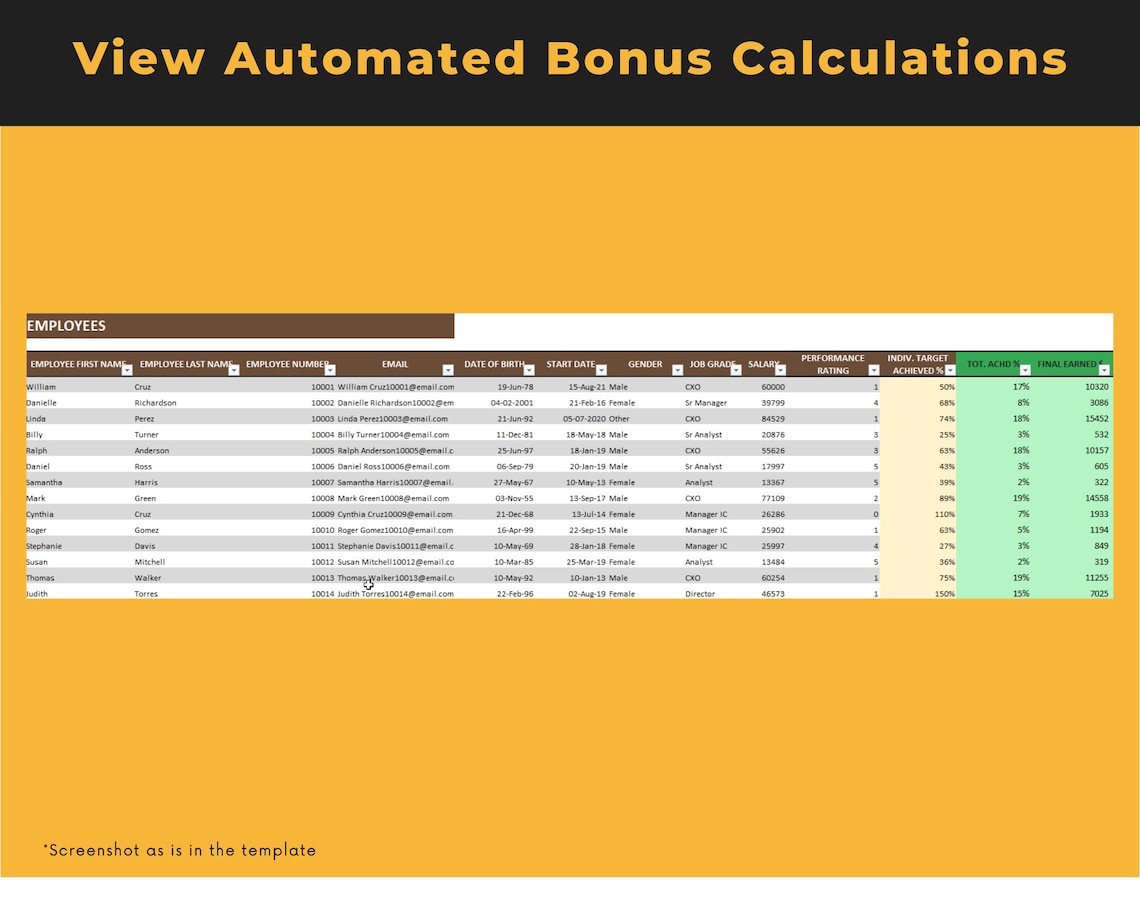
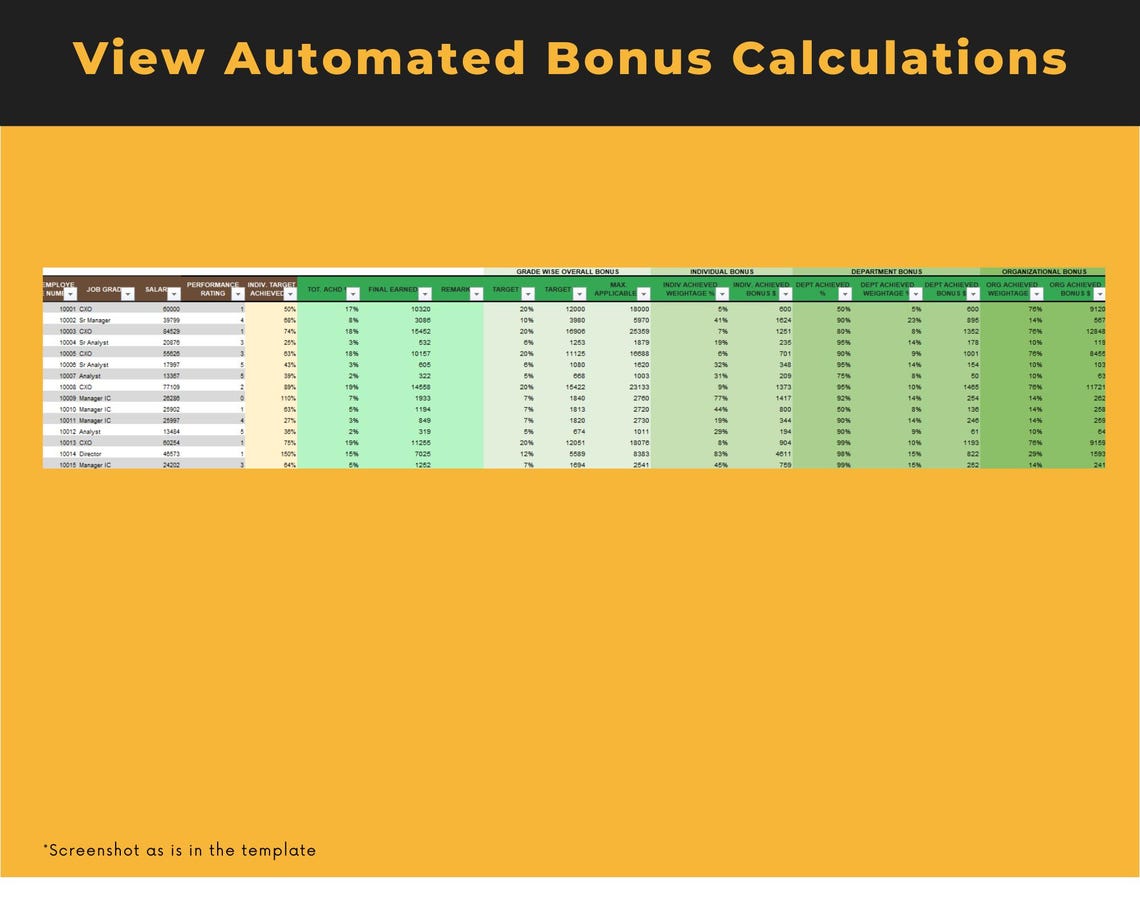
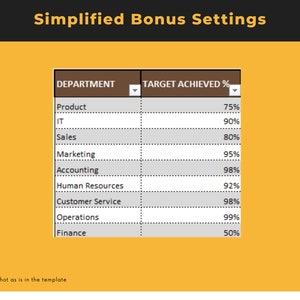
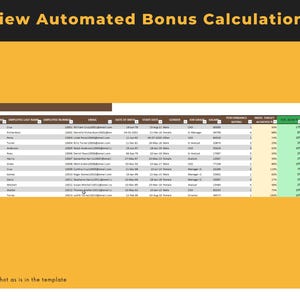
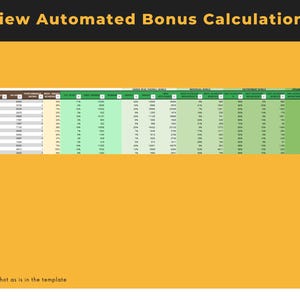
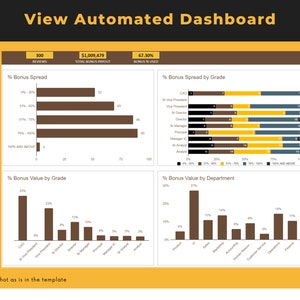
Price:BARGES88 : Bandar Resmi Situs Slot Online Gacor Hari Ini RTP Live Slot Maxwin !
BARGES88 ialah bandar judi resmi situs slot online paling gacor hari ini yang sudah menyediakan RTP live slot untuk mencapai satu tujuan maxwin di semua permainan, Rasakan sensasional di luar ataupun di dalam freespin dengan hadiah yang fantastis hanya di situs BARGES88 login sekarang juga !
You can only make an offer when buying a single item
Highlights
BARGES88 ialah bandar judi resmi situs slot online paling gacor hari ini yang sudah menyediakan RTP live slot untuk mencapai satu tujuan maxwin di semua permainan, Rasakan sensasional di luar ataupun di dalam freespin dengan hadiah yang fantastis hanya di situs BARGES88 login sekarang juga !
4.9 out of 5
(618 reviews)
All reviews are from verified buyers
Reviews for this shop
Daftar dan langsung dapet maxwin besar di RTP SLOT! Terjamin Seru banget!
Ini SLOT MAXWIN seru banget! Sekali deposit langsung dapat jackpot gede!
Di SLOT GACOR deposit sudah murah hanya 10rb dan bisa main semua slot lagi!.